Factory-Built Homes
Factory-Built Homes
What is a Factory-Built Home?
A factory-built home, often referred to as a manufactured or modular home, is a residential structure constructed entirely or predominantly in a controlled factory environment. The building process involves assembling the home in sections or modules, each crafted with precision and efficiency. Once completed, these modules are transported to the final location for assembly on-site. Factory-built homes adhere to strict construction standards and regulations, ensuring quality and safety. They offer a more streamlined and cost-effective alternative to traditional on-site construction, allowing for greater customization, quicker construction timelines, and increased efficiency in resource utilization.


Modular vs. Manufactured
Modular and manufactured housing are innovative solutions that offer alternatives to traditional site-built homes, each with distinct characteristics that cater to different preferences and needs.
KEY DIFFERENCES
Modular
Constructed in sections or modules off-site in a factory-controlled environment. These modules are then transported to the building site and assembled into a fully functional home. The construction process allows for a high degree of customization, and modular homes often comply with local building codes. They can be indistinguishable from traditional homes in terms of design and quality.
Manufactured
Built entirely in a factory and transported to the final location. They are constructed on a steel frame with wheels, enabling them to be moved if necessary. While manufactured homes meet federal construction standards, they may not always conform to local building codes, which can vary. They offer a more cost-effective and faster housing solution compared to traditional construction.
Building Codes
Modular
Typically adhere to the same local building codes as traditional homes, ensuring they meet high construction standards.
Manufactured
Comply with federal standards set by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), but local building codes may vary.
Transportability
Modular
Designed to be transported in sections and assembled on-site but are not easily moved once set up.
Manufactured
Designed to be mobile and can be relocated if needed.
Customization
Modular
Modular homes provide a higher degree of customization in terms of design, finishes, and layout, often offering options similar to traditional custom-built homes.
Manufactured
Manufactured homes may have limited customization options due to their production process and standardization.
Foundation
Modular
Manufactured
Summary
Factory-Built Homes
The Process
Communities crafted and constructed with an innovative approach at the intersection of craftsmanship, quality, and attainability.

Design and Planning
First, we choose a manufactured home design that suits your preferences and needs. Collaborate with the manufacturer to customize features within the limitations of the production process.
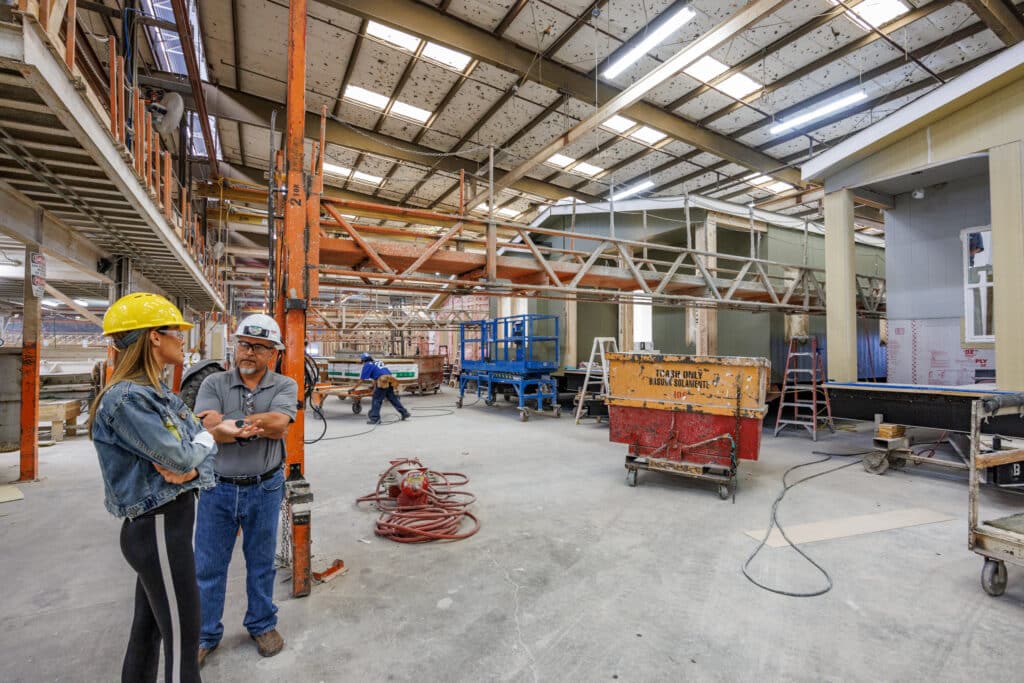
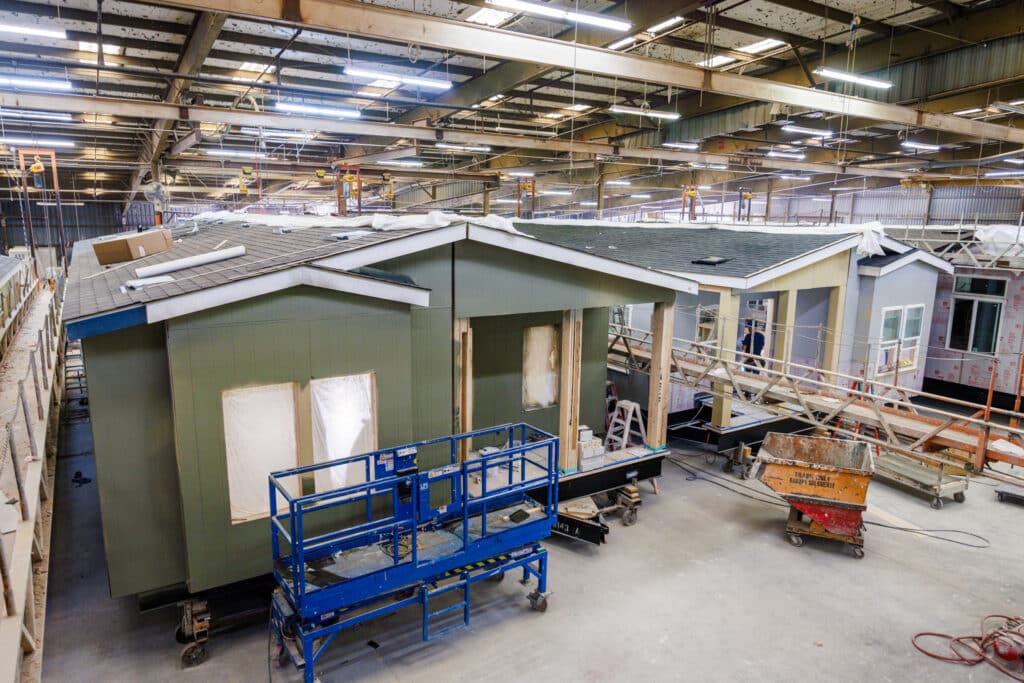
Factory Construction
The home is built entirely in a controlled factory environment on a steel frame, including: assembling the structure, installing plumbing, electrical systems, and finishing interior and exterior elements.
Quality Control
Rigorous quality checks are conducted throughout the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with federal standards and company specifications.
Transportation to Site
Once construction is complete, the manufactured home is transported to the designated site on specialized carriers.
Site Preparation
Prepare the lot by ensuring it meets local zoning and utility requirements. Install a foundation, which may include a concrete slab, piers, or a basement, depending on local regulations and personal preferences.
Installation on Foundation
The manufactured home is carefully placed on the foundation, aligning it according to design specifications.
Utility Connection
Hook up the home to local utilities such as water, electricity, and sewer systems. Ensure all connections comply with local building codes and regulations.
Interior & Exterior Finishing
Complete any remaining interior work and exterior finishing touches, such as siding, roofing, and landscaping. Connect appliances and systems to utility services and
Inspection & Compliance
Local building inspectors conduct a final inspection to ensure the manufactured home meets all relevant codes and regulations.
Occupancy
Once inspections are passed and all necessary permits are obtained, the home is ready for occupancy. The process of building and setting a manufactured home on a lot is designed for efficiency and speed, making it a viable solution to our housing crisis, offering a streamlined home construction experience, that we scale on a community level.
Our Solutions
Product Types

Single Family - Detached (SFD)
Single-family detached homes are standalone residential structures designed to house one family.
They are not connected to any other dwelling units and typically have their own private outdoor spaces, such as yards or gardens. These homes provide a high degree of privacy and independence for residents.
We design these homes in various architectural styles and sizes in compliance with local building codes and HUD standards.

Single Family - Attached (SFA)
Each unit has its own entrance and outdoor space. While they are attached to neighboring homes, they offer more privacy than traditional apartment buildings.

Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU)
Accessory Dwelling Units, or ADUs, are secondary housing units located on the same property as a single-family home. ADUs can take various forms, including detached structures, converted garages, or attached additions to the main house.
They are designed to provide supplementary living space and can be used for purposes such as accommodating relatives, renting out for extra income, or as a home office. ADUs are subject to local zoning and building regulations, and their usage and size can vary depending on the jurisdiction’s rules.
They offer flexibility in housing options and can help address issues related to housing shortages or multigenerational living.
Articles & Research
Featured Articles
Population growth could stop and metro Denver would still have a housing shortfall
The Denver metro area is experiencing a rise in apartment...
2024 Demographia Report Reveals Stark Housing Affordability Challenges
The 2024 edition of the Demographia International Housing Affordability report...
El Futuro es Latino
From the earliest days of European settlement, Latinos have played...


